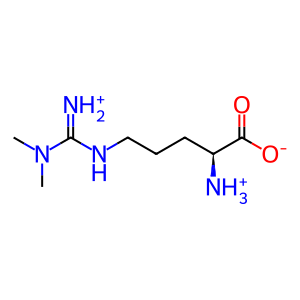
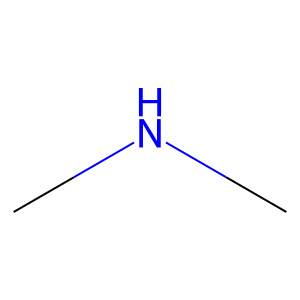
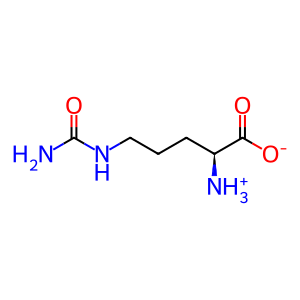
Reaction: DDAH1,2 hydrolyses ADMA to DMA and L-Cit
- in pathway: eNOS activation
N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1 (DDAH1) plays a role in the regulation of nitric oxide generation by catalyzing the hydrolysis an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), N(omega),N(omega)-dimethyl-L-arginine (ADMA) to dimethylamine (DMA) and L-citrulline (L-Cit) (Forbes et al. 2008, Wang et al. 2009). DDAH2, an isoform of DDAH1 previously thought to catalyze this reaction (Cillero-Pastor et al. 2012) has recently been shown to have no detectable catalytic activity against ADMA under conditions in which DDAH1 is active (Ragavan et al. 2023).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
DMA [cytosol]
L-Cit [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ADMA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5693373
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
N(omega),N(omega)-dimethyl-L-argininium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
dimethylamine
L-citrulline zwitterion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5693373