Reaction: CES1 trimer.CES2 hydrolyse COCN to BEG
- in pathway: Phase I - Functionalization of compounds
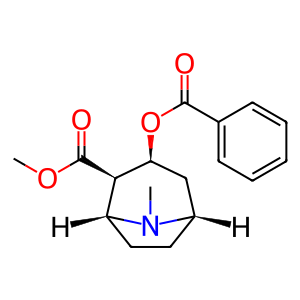
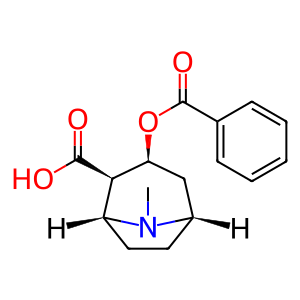
Cocaine (COCN) is an addictive, psychoactive alkaloid that is primarily inactivated by hydrolysis to benzoylecgonine (BEG), the major urinary metabolite of the drug. Human liver carboxylesterases 1 and 2 (CES1 and 2), located in the ER lumen, are involved in the detoxification of xenobiotics and can hydrolyse COCN to BEG (Brzezinski et al. 1994, Pindel et al. 1997). CES1 is functional as a homotrimer or homohexamer (Bencharit et al. 2003) whereas CES2 is monomeric.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
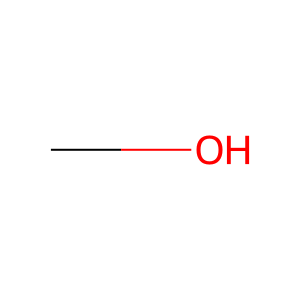
MeOH [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
BEG [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
H2O [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
COCN [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5693691
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
cocaine
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
methanol
ecgonine benzoate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5693691