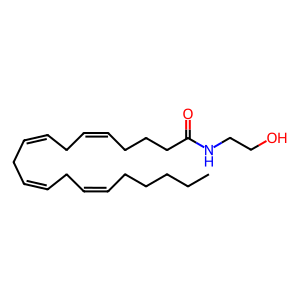
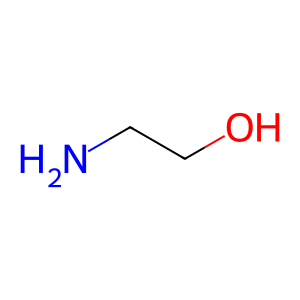
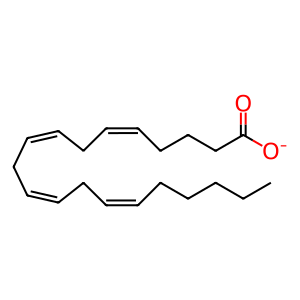
Reaction: FAAH hydrolyses AEA to AA and ETA
- in pathway: Arachidonic acid metabolism
Fatty acid amides are a class of lipid transmitters that include the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide (AEA) and the sleep-inducing chemical oleamide. The magnitude and duration of their signalling are controlled by enzymatic hydrolysis mediated by fatty-acid amide hydrolases 1 and 2 (FAAH, H2). Hydrolysis of AEA is described here (Wei et al. 2006). FAAH is localised to the ER membrane whereas FAAH2 is localised to lipid droplets (Kaczocha et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
ETA [cytosol]
AA [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
AEA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5693742
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
anandamide
Reaction output - small molecules:
ethanolamine
arachidonate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5693742