Reaction: PXLP-K754-GLDC dimer decarboxylates Gly
- in pathway: Glycine degradation
The simplest amino acid, glycine, is catabolised by several different pathways. The major pathway is via the glycine cleavage system. In the first reaction, glycine (Gly) is decarboxylated to carbon dioxide (CO2) and aminomethyl group (NH2CH2) by mitochondrial glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (GLDC, P protein), a dimeric protein using pyridoxal 5-phosphate (PXPL) as cofactor per subunit (Kume et al. 1991). Mitochondrial glycine cleavage system H protein (GCSH) is used as a co-substrate in this reaction. GCSH uses lipoate as a cofactor which accepts the aminomethylgroup from glycine decarboxylation to form a S-aminomethyldihydrolipoylated protein (GCSH:SAMDLL) (Fujiwara et al. 1991, Fujiwara et al. 1991).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CO2 [mitochondrial matrix]
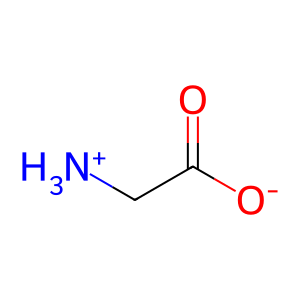
Gly [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5693967
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
glycine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5693967