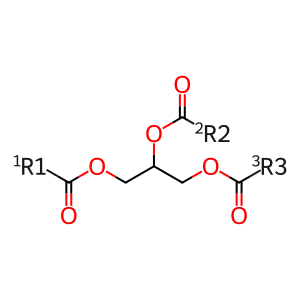
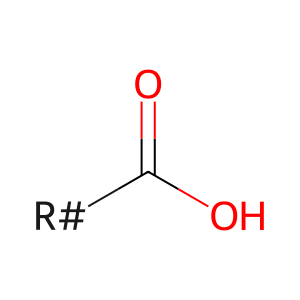
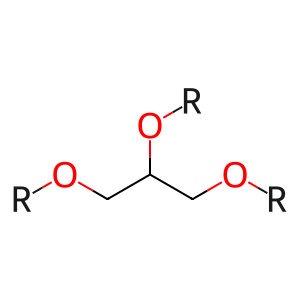
Reaction: LIPC dimer hydrolyses TAG to DAG and FA
- in pathway: Assembly of active LPL and LIPC lipase complexes
Fatty acids (FAs) are used as energy substrates and are stored as triglycerides. Triacylglycerol (TAG) has to be cleaved by lipases to be able to move in and out of cells for usage. Hepatic triacylglycerol lipase (LIPC) is one of several enzymes that catalyses the hydrolysis of TAGs to free fatty acids (FAs) and diacylglycerol (DAG) (Hegele et al. 1993, Santamarina-Fojo et al. 2004). Defects in LIPC can cause hepatic lipase deficiency (HL deficiency; MIM:614025), a disorder characterised by premature atherosclerosis and abnormal circulating lipoproteins (Hegele et al. 1992, 1993).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
FAs [extracellular region]
DAGs [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
TAGs [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5694109
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
triglyceride
Reaction output - small molecules:
fatty acid
diglyceride
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5694109