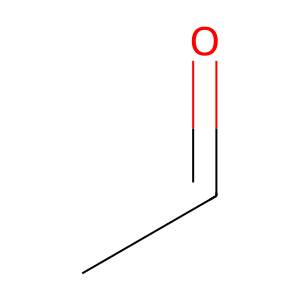
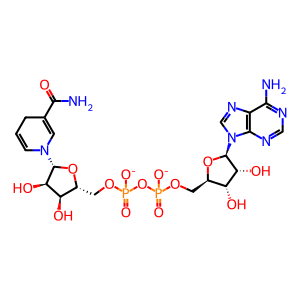
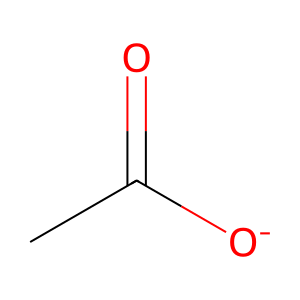
Reaction: ALDH1B1 tetramer oxidises CH3CHO to CH3COOH
- in pathway: Ethanol oxidation
Ethanol-induced organ damage is attributed to its toxic metabolite acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) therefore metabolism and elimination of this metabolite is important for cellular defence. Mitochondrial ALDH1B1 is one of several human ALDHs that can oxidise CH3CHO to acetic acid (CH3COOH) (Stagos et al. 2010). ALDH1B1 is thought to function as a homotetramer.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
NADH [mitochondrial matrix]
CH3COO- [mitochondrial matrix]
CH3CHO [mitochondrial matrix]
NAD+ [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5696091
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetaldehyde
NAD(1-)
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
NADH(2-)
acetate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5696091