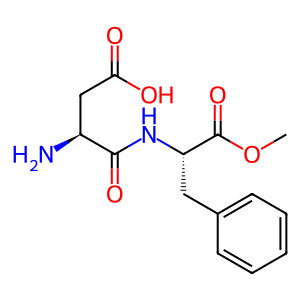
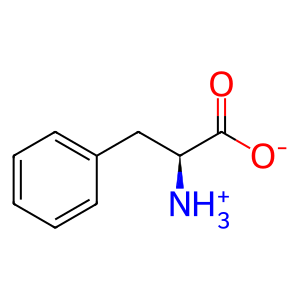
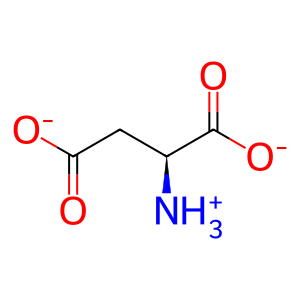
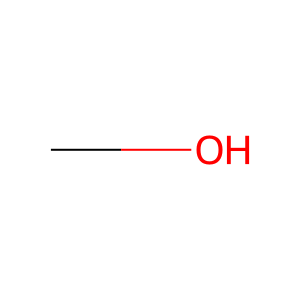
Reaction: ASRGL1 hydrolyses aspartame to L-Asp, L-Phe
- in pathway: Phenylalanine metabolism
The human isoaspartyl peptidase/L-asparaginase (ASRGL1) is an N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) hydrolase superfamily member that catalyses the hydrolysis of l-asparagine and beta-aspartyl-dipeptides and their methyl esters such as aspartame (beta-L-Asp-L-Phe methyl ester) (Cantor et al. 2009, Li et al. 2012, Nomme et al. 2014). ASRGL1 is a cytosolic enzyme that is active as a heterodimer of alpha and beta chains, formed by autocleavage between Gly167 and Thr168 (Nomme et al. 2012). ASRGL1 is expressed in brain, kidney, testis and the gastrointestinal tract. Aspartame is an artificial sweetner used as a sugar substitute in some drinks. Sufferers of phenylketonuria (PKU) are advised to avoid aspartame as one of its breakdown products, phenylalanine, could contribute to the excess pool of phenylalanine that PKU sufferers cannot metabolise from the body.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
L-Phe [cytosol]
L-Asp [cytosol]
MeOH [cytosol]
aspartame [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5696365
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
aspartame
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-phenylalanine zwitterion
L-aspartate(1-)
methanol
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5696365