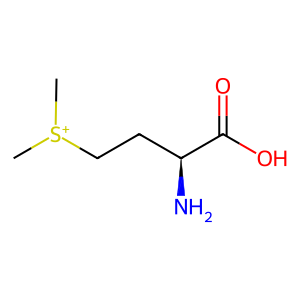
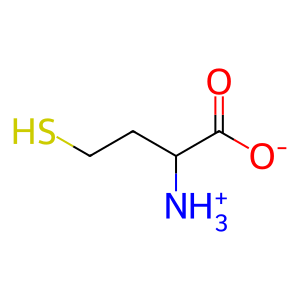
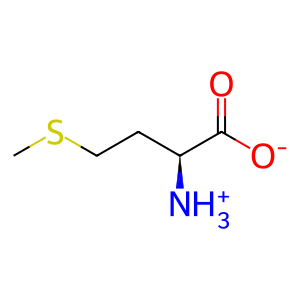
Reaction: BHMT2 tetramer transfers CH3 group from SMM to LHCYS
- in pathway: Sulfur amino acid metabolism
L-homocysteine (LHCYS) is derived from L-methionine (L-Met) and can either be remethylated to reform L-Met or take part in cysteine biosynthesis via the trans-sulfuration pathway. LHCYS remethylation can occur by the action of two enzymes; cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase and betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase, using methyltetrahydrofolate and betaine respectively as methyl donors. A third enzyme, S-methylmethionine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase (BHMT2), can use S-methylmethionine (SMM) as the methyl donor to methylate LHCYS and reform L-Met. BHMT2 is a tetrameric, cytosolic enzyme that requires one Zn2+ ion per subunit as cofactor (Szegedi et al. 2008).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
L-Met [cytosol]
SMM [cytosol]
HCYS [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5696838
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
S-methyl-L-methionine
homocysteine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
L-methionine zwitterion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5696838