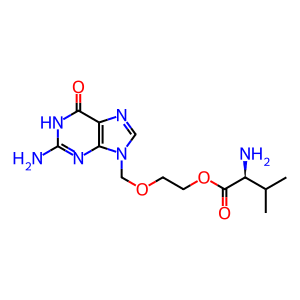
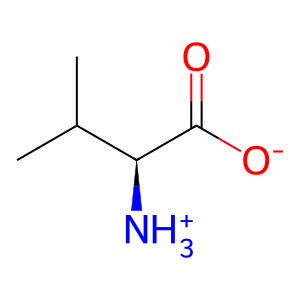
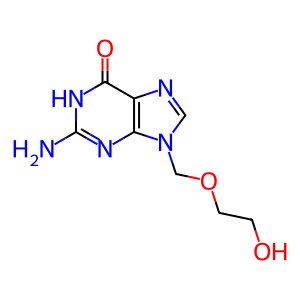
Reaction: BPHL hydrolyses VACV to ACV
- in pathway: Phase I - Functionalization of compounds
Valacyclovir (VACV) is the 5'-valyl ester prodrug of acyclovir (ACV), an effective anti-herpetic drug. Systemic bioavailability of ACV in humans is up to five times higher when administered orally as the prodrug. After intestinal absorption, valacyclovir hydrolase (BPHL) mediates the rapid and complete hydrolysis to VACV to ACV (Kim et al. 2003, Lai et al. 2008). The subcellular location of human BPHL is unknown but rat Bhpl localises to the mitochondrial membrane (Kim et al. 2003).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
L-Val [cytosol]
ACV [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
VACV [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6784959
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
valacyclovir
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-valine zwitterion
acyclovir
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6784959