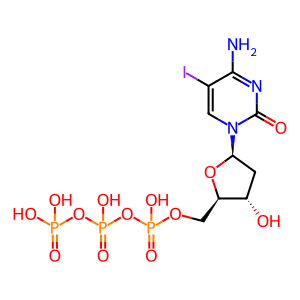
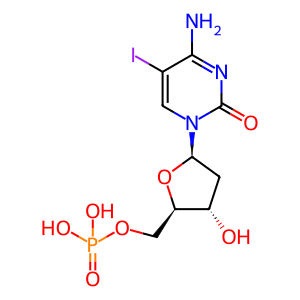
Reaction: DCTPP1 hydrolyses 5idCTP
- in pathway: Interconversion of nucleotide di- and triphosphates
Human dCTP pyrophosphatase 1 (DCTPP1) is a cytosolic enzyme able to hydrolyse deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) to their corresponding nucleoside monophosphates. DCTPP1 probably plays a role in protecting DNA or RNA against the incorporation of modified nucleotide triphosphates. Based on mouse studies, Dctpp1 has strong preference for modified dCTPs, with highest activity shown towards 5-iodo-dCTP (5idCTP) (Nonaka et al. 2009). Crystal structures of mouse Dctpp1 suggest it functions as a homotetramer and requires two or three Mg2+ ions per subunit (Wu et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
5idCMP [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
5idCTP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6786257
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
5-iododeoxycytidine triphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
hydron
5-iododeoxycytidine monophosphate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6786257