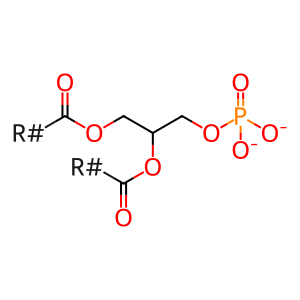
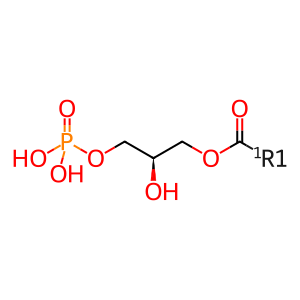
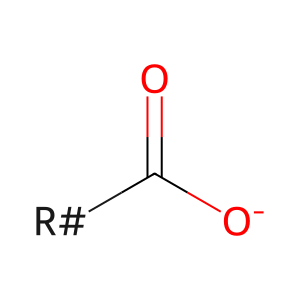
Reaction: DDHD1,2 hydrolyse PA
- in pathway: Synthesis of PA
Glycerophospholipids are important structural and functional components of biological membranes, of serum lipoproteins and pulmonary surfactant and act as precursors of lipid mediators such as platelet-activating factor and eicosanoids. Phosphatidic acid (PA) is a common glycerophospholipid and its hydrolysis can mediate its functions described above. Phospholipases DDHD1 and 2 can mediate the hydrolysis of PA (Inoue et al. 2012, Nakajima et al. 2002). Defects in DDHD1 or DDHD2 can cause autosomal recessive spastic paraplegias 28 or 54 respectively (SPG28, MIM:609340; SPG54, MIM:615033). These are forms of neurodegenerative spastic paraplegia, characterised by slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs (Tesson et al. 2012, Schuurs-Hoeijmakers et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
1-acyl LPA [plasma membrane]
LCFA(-) [plasma membrane]
H2O [cytosol]
PA [plasma membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6786650
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
phosphatidate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
1-acyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate
long-chain fatty acid anion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6786650