Reaction: TRMU (MTO2, MTU1) transfers a sulfur atom to 5-taurinomethyluridine-34 in tRNA
- in pathway: tRNA modification in the mitochondrion
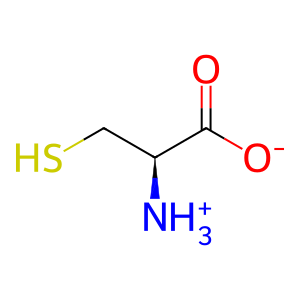
TRMU (MTU1) transfers a sulfur atom from L-cysteine to the 2 position of 5-taurinomethyluridine-34 in tRNAs (Umeda et al. 2005, Sasarman et al. 2011). In Escherichia coli the sulfur is transferred along a relay system of proteins from L-cysteine to uridine. It is unknown if such a relay system also exists in humans. In yeast, mutations in MTU1, the homolog of TRMU act synergistically with mutations in the homologs of GTPBP3 and MTO1 to impair mitochondrial function (Umeda et al. 2005). In humans mutations in TRMU cause mitochondrial infantile liver disease (Zeharia et al. 2009, Gaignard et al. 2013), infantile respiratory chain disease (Boczonadi et al. 2013), and modify the severity of deafness associated with mutations in mitochondrial 12S rRNA (Guan et al. 2006), however abrogation of the thiouridylase function of TRMU may not be responsible for the phenotypes (Sasarman et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
L-Cys [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6787447
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-cysteine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6787447