Reaction: Membrane-bound myeloperoxidase (MPO) produces hypochlorous acid (HOCl)
Granule-derived cationic MPO protein can attach to negatively charged proteins and membrane epitopes of ingested bacteria (Selvaraj RJ et al. 1978; Miyasaki KT et al. 1987). This could be a way of directing HOCl for effective killing (Klebanoff SJ et al. 1999).
MPO is a heme enzyme that uses hydrogen peroxide to oxidize chloride to hypochlorous acid. MPO reacts with hydrogen peroxide, which is produced by stimulated neutrophils, to form the redox intermediate compound I (Winterbourn CC et al 2006; Davies MJ 2011; Pattison DI et al. 2012). Compound I is strongly oxidizing and reacts with a variety of substrates such as halide and pseudo-halide ions to produce hypohalous acids (HOX where X = Cl, Br, SCN). Its main physiological substrate is assumed to be chloride, which undergoes a two-electron oxidation to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl) (Winterbourn CC et al 2006; Davies MJ 2001; Pattison DI et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
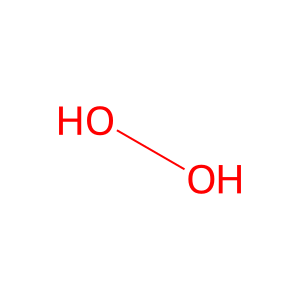
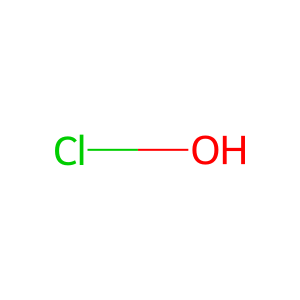
HOCl [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
H2O2 [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
Cl- [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
H+ [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6789031
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydrogen peroxide
chloride
hydron
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
hypochlorous acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6789031