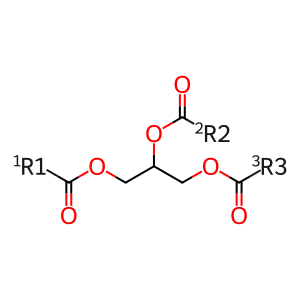
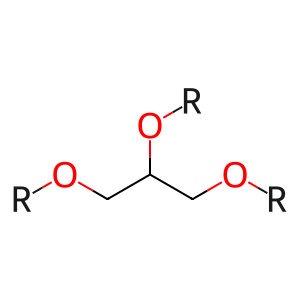
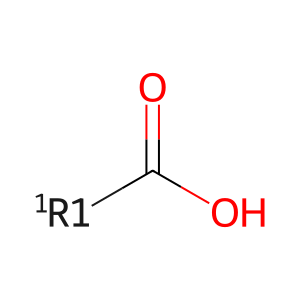
Reaction: LIPs hydrolyse TG to DAG and RCOOH
- in pathway: Formation of the cornified envelope
Lipases are enzymes that hydrolyse dietary lipids such as fats, oils and triglycerides. The majority of human lipases are secreted by the pancreas and function mainly in the digestive system. Lipase members K, M and N (LIPK, M and N), however, all appear to play a role in the last step of keratinocyte differentiation where they are proposed to hydrolyse triglycerides to free fatty acids and glycerol which is essential to stratum corneum hydration (Toulza et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
DAGs [extracellular region]
RCOOH [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
TAGs [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6789310
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
triglyceride
Reaction output - small molecules:
diglyceride
carboxylic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6789310