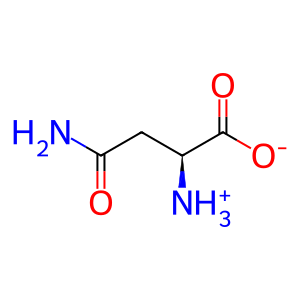
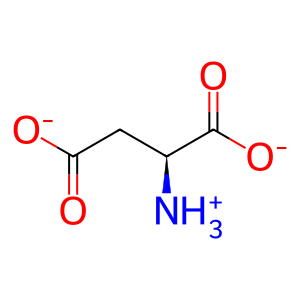
Reaction: ASPG hydrolyses L-Asn to L-Asp
- in pathway: Aspartate and asparagine metabolism
L-Asparaginases can catalyse the hydrolysis of L-asparagine (L-Asn) to L-aspartic acid (L-Asp) and ammonia (NH3) in organisms ranging from bacteria to humans. Bacterial type II versions of the enzyme serve as therapeutics for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia despite adverse side effects. The human equivalent (60 kDa lysophospholipase, ASPG) has shown to possess L-Asparaginase activity and may be a potential alternative replacement for bacterial enzymes as a leukemia therapeutic in the future (Karamitros & Konrad 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
L-Asp [cytosol]
NH3 [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
L-Asn [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6797627
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
L-asparagine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-aspartate(1-)
ammonia
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6797627