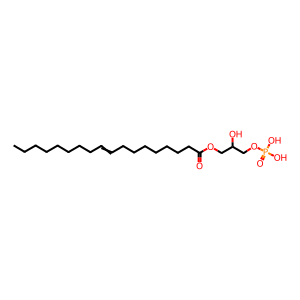
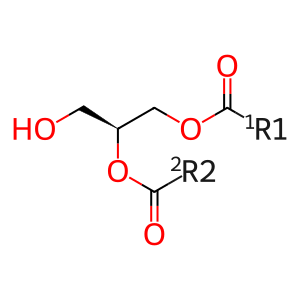
Reaction: LRPP4(LRPP1-3,5) hydrolyse LPA
- in pathway: Lysosphingolipid and LPA receptors
Human plasticity-related genes (PRGs, lipid phosphate phosphatase-related proteins LPPRs) comprise 5 members expressed in the CNS. They are membrane-spanning enzymes thought to mediate the extracellular concentration and signal transduction of lipid phosphate esters such as lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and spingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) by hydrolysing their phosphate groups. LPPR4 has been shown to act as an ecto-enzyme in axon growth and regenerative sprouting by mediating LPA levels (Brauer et al. 2003). The activity of the other LPPR members has yet to be defined (Strauss & Brauer 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [extracellular region]
1,2-DAG [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
LPA [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6797630
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
1-octadec-9-enoylglycero-3-phosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6797630