Reaction: DMGDH:FAD oxidatively demethylates DMGLY to SARC
- in pathway: Choline catabolism
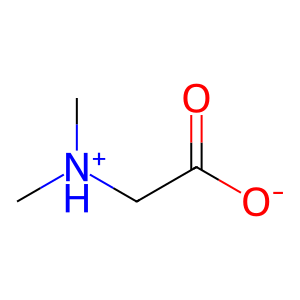
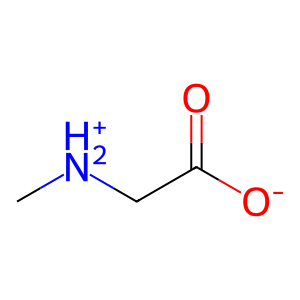
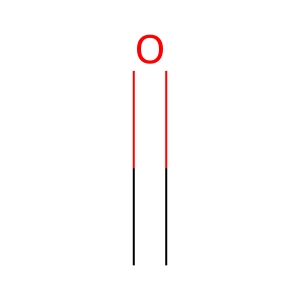
Mitochondrial dimethylglycine dehydrogenase (DMGDH) is an enzyme involved in the choline catabolic pathway, mediating the oxidative demethylation of dimethylglycine (DMGLY) to form sarcosine (SARC, aka methylglycine, MeGly) and formaldehyde (CH2O), an active 1-carbon unit (Binzak et al. 2000). DMGDH covalently binds one FAD cofactor per monomer. Defects in DMGDH cause DMGDH deficiency (DMGDHD; MIM:605850), a disorder characterised by a fishy odour and muscle fatigue with increased serum creatine kinase. Biochemically, increased levels of DMGLY are detected in the serum and urine (Binzak et al. 2001).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
SARC [mitochondrial matrix]
CH2O [mitochondrial matrix]
DMGLY [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6797653
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
N,N-dimethylglycine zwitterion
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
sarcosine zwitterion
formaldehyde
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6797653