Reaction: ALDH7A1 oxidises BETALD to BET
- in pathway: Choline catabolism
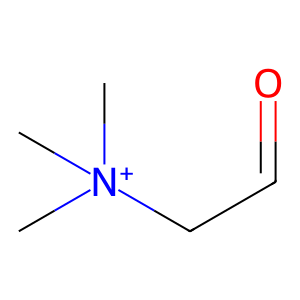
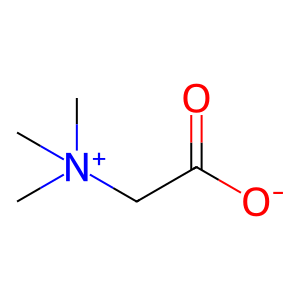
Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH7A1) is a multifunctional enzyme present in mitochondria, nucleus and the cytosol and plays an important role in protecting against hyperosmotic stress and metabolising toxic aldehydes. It is able to oxidise the osmolyte precursor betaine aldehyde (BETALD) to betaine (BET) (as well as the intermediate lysine degradation product, alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde, not shown here) (Brocker et al. 2010). The mitochondrial isoform of ALDH7A1 is shown here.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
BET [mitochondrial matrix]
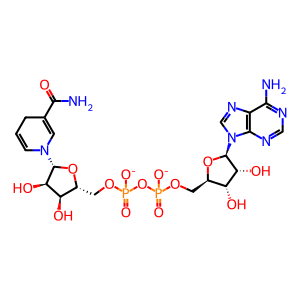
NADH [mitochondrial matrix]
NAD+ [mitochondrial matrix]
BETALD [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6797955
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
NAD(1-)
betaine aldehyde
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
glycine betaine
NADH(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6797955