Reaction: GLYCTK phosphorylates DGA to 3PDGA
- in pathway: Fructose catabolism
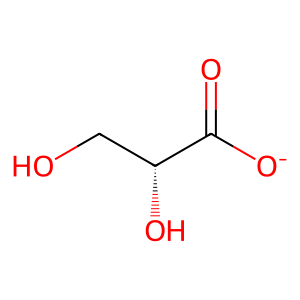
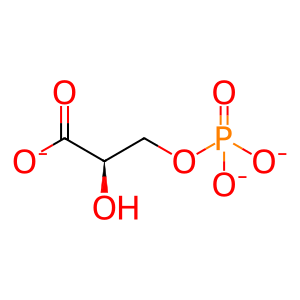
D-glyceric acid (DGA) is an intermediate of serine catabolism and of a minor pathway of fructose metabolism. The only known fate of DGA is phosphorylation to 3-phospho-D-glyceric acid (3PDGA) by cytosolic glycerate kinase (GLYCTK) (Yu et al. 2006). Defects in GLYCTK can cause D-glyceric aciduria (D-GA; MIM:220120), a rare inborn error of serine and fructose metabolism where DGA is excreted in large amounts in the urine. A variable phenotype is observed, ranging from severe mental retardation and death to milder speech delays and normal development (Van Schaftingen 1989, Sass et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
3PDGA [cytosol]
DGA [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6799495
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
D-glycerate
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
ADP(3-)
3-phosphonato-D-glycerate(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6799495