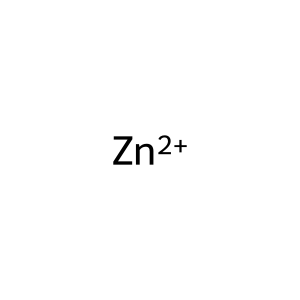Reaction: DCD forms oligomeric complex
- in pathway: Antimicrobial peptides
DCD peptide is initially monomeric when secreted in human sweat. In presence of a negatively charged bacterial membrane the cationic N-terminus of DCD gets attracted electrostatically (Paulmann M et al. 2012). Upon interaction with the bacterial membrane a change in the secondary structure from random coil to an alpha-helical conformation is induced. DCD-1(L) self-assembles into a higher oligomeric state which is stabilized by zinc ions. Subsequently, by oligomerization DCD is able to form ion channels in the bacterial membrane resulting in bacterial cell death ( (Paulmann M et al. 2012; Song C et al. 2013; Burian M & Schittek B 2015).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Zn2+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6803104
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
zinc(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6803104