Reaction: NAAA hydrolyses NAEs to FAs and ethanolamine
- in pathway: Neurotransmitter release cycle
N-acylethanolamines (NAEs) are bioactive lipid molecules present in animals and plants. N-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase (NAAA), a heterodimeric lysosomal enzyme is able to hydrolyse NAEs to their respective fatty acids (FAs) and ethanolamine (ETA). The NAEs N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide), N-palmitoylethanolamine, and N-oleoylethanolamine possess cannabimimetic activity, anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities, and anorexic activity, respectively. NAAA can mediate their endogenous levels and shows greatest affinity for N-palmitoylethanolamine (Hong et al. 1999, Tsuboi et al. 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
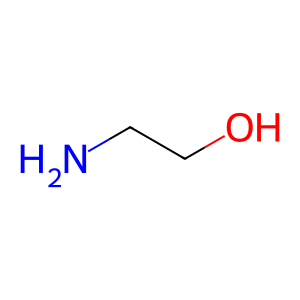
ETA [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6803753
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
ethanolamine
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6803753