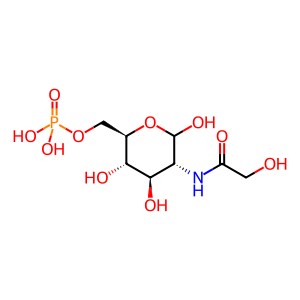
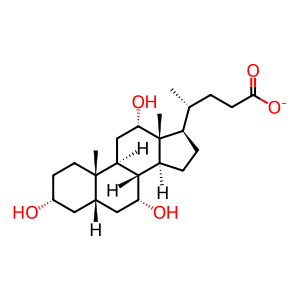
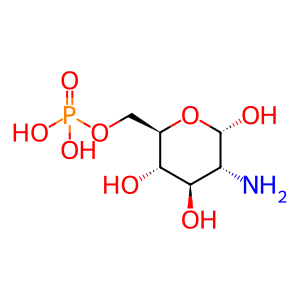
Reaction: AMDHD2 hydrolyses GlcNGc-6-P to GlcN6P and CCA
- in pathway: Synthesis of UDP-N-acetyl-glucosamine
Humans are not able to catalyse the formation of N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) due to an inactive CMAHP enzyme. Neu5Gc can be obtained from dietary sources and must be degraded to avoid accummulation and resultant chronic inflammation known as xenosialitis (Varki et al. 2011). In the Neu5Gc degradation pathway, the putative N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate deacetylase (AMDHD2) is thought to irreversibly hydrolyse N-glycolylglucosamine 6-phosphate (GlcNGc-6-P), resulting in the ubiquitous metabolites glycolate (CCA) and glucosamine 6-phosphate (GlcN6P) (Bergfeld et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CCA [cytosol]
GlcN6P [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
GlcNGc-6-P [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6803789
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
N-glycoloyl-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
cholate
alpha-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6803789