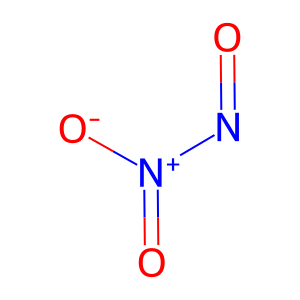
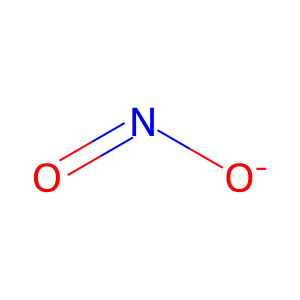
Reaction: S-nitrosylation of cysteine residues in proteins by N2O3
- in pathway: ROS and RNS production in phagocytes
S-nitrosylation (SNO) is a selective post-translational protein modification that is mediated by nitric oxide radicals. SNO involves the covalent attachment of nitric oxide (NO) to the sulfur atom of cysteine to produce an S-N=O adduct. SNO critically regulates protein activity, localization and stability (Broniowska KA & Hogg N 2012; Ali AA et al. 2013)
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Nitrite [cytosol]
N2O3 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6803978
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dinitrogen trioxide
Reaction output - small molecules:
nitrite
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6803978