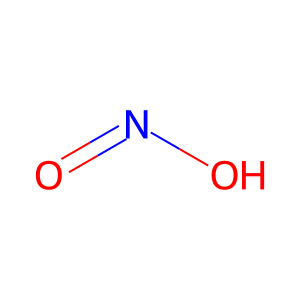
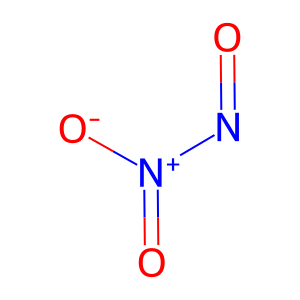
Reaction: HNO2 produces N2O3
- in pathway: ROS and RNS production in phagocytes
In the acidic conditions nitrite (NO2-) and nitrous acid (HNO2) present as a conjugated acid-base pair. HNO2 can further react with an additional HNO2 to produce N2O3 (Oldreive C & Rice-Evans C. 2001). N2O3 formation regulates the function of many target proteins through the coupling of a nitroso moiety (NO+) to a reactive cysteine, ultimately leading to the formation of RSNO, a process commonly known as S-nitrosylation (Broniowska KA & Hogg N 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
N2O3 [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
HNO2 [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6803999
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
nitrous acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
dinitrogen trioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6803999