Reaction: EHHADH hydrates trans-2,3-dehydrohexacosanoyl-CoA
- in pathway: Beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids
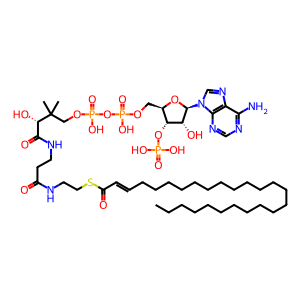
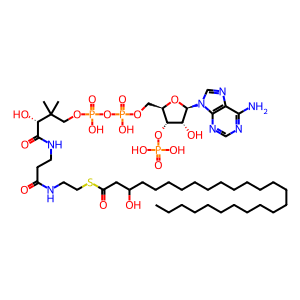
Peroxisomal EHHADH catalyzes the reaction of trans-2,3-dehydrohexacosanoyl-CoA and H2O to form 3-hydroxyhexacosanoyl-CoA. The enzyme is bifunctional - an aminoterminal domain catalyzes the dehydrogenation of a variety of 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA's and a carboxyterminal domain catalyzes the hydration of a variety of trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA's, the reaction annotated here. The properties of the human enzyme are inferred from studies of its mouse and rat homologues and from enzymatic stdies of mutant yeast cells expressing the cloned human enzyme (Chen et al. 1991, Ferdinandusse et al. 2004; Houten et al. 2012; Lalwani et al. 1981; Osumi & Hashimoto 1979). The enzyme can also act on fatty dicarboxylic acids (not annotated here) (Houten et al, 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
3-hydroxyhexacosanoyl-CoA [peroxisomal matrix]
H2O [peroxisomal matrix]
trans-2,3-dehydrohexacosanoyl-CoA [peroxisomal matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6809263
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
trans-2-hexacosenoyl-CoA
Reaction output - small molecules:
3-hydroxyhexacosanoyl-CoA
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6809263