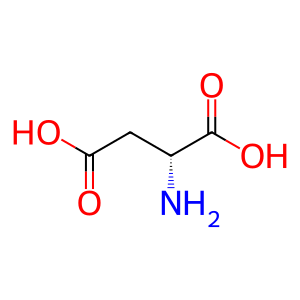
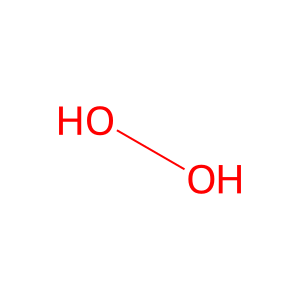
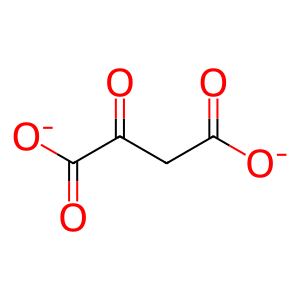
Reaction: DDO oxidizes D-Asp to OA
- in pathway: Glyoxylate metabolism and glycine degradation
Peroxisomal DDO (D-aspartate oxidase) catalyzes the oxidation of D-Asp (D-aspartate) to OA (oxaloacetate) with the formation of H2O2. The human enzyme is a monomer with an FAD cofactor (Katane et al. 2010, 2015; Setoyama & Miura 1997), as is its well-characterized bovine homolog (Negri et al. 1992). Its peroxisomal location is inferred from studies in cultured cells of fusion proteins containing the carboxyterminal peptide sequence of DDO (Amery et al. 1998).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O2 [peroxisomal matrix]
NH4+ [peroxisomal matrix]
OA [peroxisomal matrix]
O2 [peroxisomal matrix]
H2O [peroxisomal matrix]
D-Asp [peroxisomal matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6810076
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
water
D-aspartic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogen peroxide
ammonium
oxaloacetate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6810076