Reaction: NCEH1 hydrolyzes cholesterol esters
- in pathway: LDL clearance
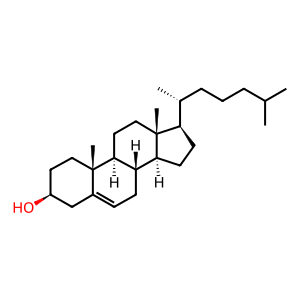
NCEH1 (neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase) hydrolyzes cholesterol esters to form cholesterol (CHOL) and free fatty acids (LCFA). In both humans (Igarashi et al. 2010a) and mice (Igarashi et al. 2010b, Okazaki et al. 2008, Sakai et al. 2014 ) NCEH1 associated with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane appears to play a major role in cholesterol ester hydrolysis in macrophages. Free CHOL is transported via transport vesicles and can be used for cellular functions or removed from the cell by ABCA1 to create new HDL particles.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
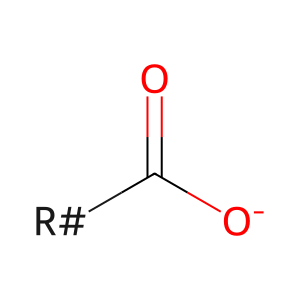
LCFA(-) [cytosol]
CHOL [transport vesicle membrane]
H2O [cytosol]
CHEST [lipid droplet]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6813720
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
cholesteryl ester
Reaction output - small molecules:
long-chain fatty acid anion
cholesterol
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6813720