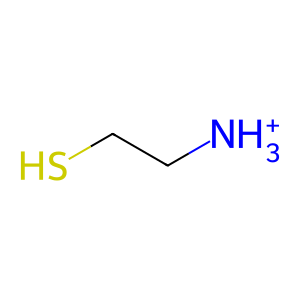
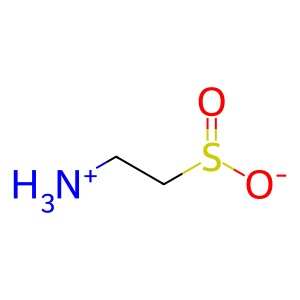
Reaction: ADO oxidises 2AET to HTAU
- in pathway: Degradation of cysteine and homocysteine
Cysteine metabolism to its sulfoxidation end-products is dependent upon two iron-dependent enzymes that are the only known mammalian thiol dioxygenases. These two thiol dioxygenases are cysteine dioxygenase (CDO) and 2-aminoethanethiol dioxygenase (ADO, cysteamine dioxygenase ). Both of these thiol dioxygenases are essential for hypotaurine and taurine biosynthesis. ADO adds molecular oxygen to the sulfhydryl group of 2-aminoethanethiol (2AET, cysteamine) to form the sulfinic acid hypotaurine (HTAU) (Dominy et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
HTAU [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
2AET [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6814153
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
cysteaminium
Reaction output - small molecules:
hypotaurine zwitterion
hydron
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6814153