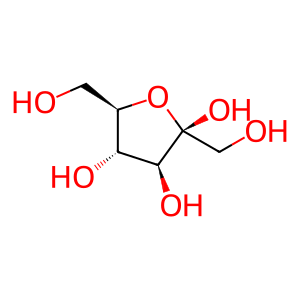
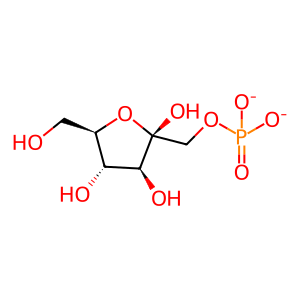
Reaction: KHK dimer phosphorylates Fru to Fru 1-P
- in pathway: Fructose catabolism
Cytosolic ketohexokinase (KHK, also known as fructokinase) catalyzes the reaction of D-fructose (Fru) and ATP to form D-fructose 1-phosphate (Fru 1-P) and ADP. Two isoforms of the enzyme, A and C, are encoded by alternatively spliced forms of the gene; both form catalytically active dimers. The C isoform is predominant in liver and kidney tissues, has high affinity for fructose, and is probably responsible for the bulk of fructose phosphorylation in vivo (Asipu et al. 2003; Trinh et al. 2009). The A isoform is found in lower levels in many other tissues and may serve a role in fructose metabolism outside of liver and kidney (Funari et al. 2005). The physiological role of KHK has been established from metabolic and DNA sequencing studies of patients with essential fructosuria (Bonthron et al. 1994) and in mouse models for this disease (Diggle et al. 2010; Ishimoto et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
beta-D-Fru 1-P [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
beta-D-Fru [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70333
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
beta-D-fructofuranose
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
ADP(3-)
beta-D-fructofuranose 1-phosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70333