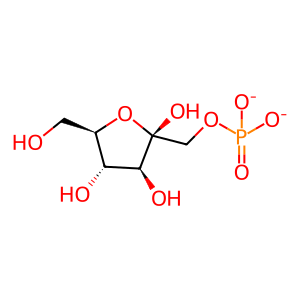
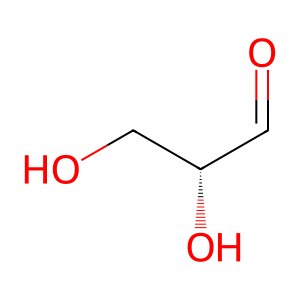
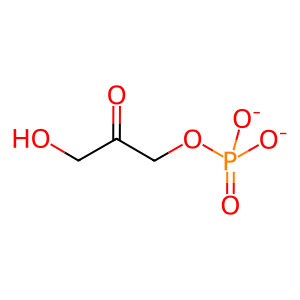
Reaction: ALDOB tetramer cleaves Fru-1-P to GA and DHAP
- in pathway: Fructose catabolism
Cytosolic aldolase B (ALDOB) catalyzes the reaction of D-fructose 1-phosphate (Fru 1-P) to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and D-glyceraldehyde (GA) (Hers & Kusaka 1953; Schapira 1975). The active form of the enzyme is a tetramer (Dalby et al. 2001). Deficiencies in the enzyme are associated with hereditary fructose intolerance in vivo (e.g., Tolan 1995; Ali et al. 1998).
ALDOB is the same aldolase isoform that catalyzes the reversible cleavage of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in glycolysis. This isoform, found in liver, kidney, and intestine, is approximately equally active with fructose 1 phosphate and fructose 1,6 bisphosphate as substrates at saturating concentrations, while the muscle and brain isoforms (ALDOA and ALDOC, respectively), have little activity with fructose-1-phosphate (Lebherz & Rutter 1969; Penhoet et el. 1969).
ALDOB is the same aldolase isoform that catalyzes the reversible cleavage of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in glycolysis. This isoform, found in liver, kidney, and intestine, is approximately equally active with fructose 1 phosphate and fructose 1,6 bisphosphate as substrates at saturating concentrations, while the muscle and brain isoforms (ALDOA and ALDOC, respectively), have little activity with fructose-1-phosphate (Lebherz & Rutter 1969; Penhoet et el. 1969).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
GA [cytosol]
DHAP [cytosol]
beta-D-Fru 1-P [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70342
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
beta-D-fructofuranose 1-phosphate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
D-glyceraldehyde
glycerone phosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70342