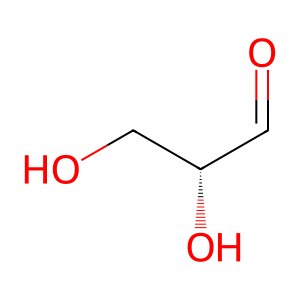
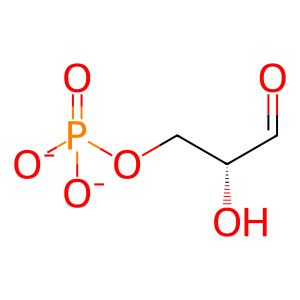
Reaction: DAK dimer phosphorylates D-glyceraldehyde to form D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
- in pathway: Fructose catabolism
Cytosolic dihydroxyacetone kinase (DAK) catalyzes the reaction of ATP and D-glyceraldehyde (GA) to form ADP and D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GA3P). This reaction was originally characterized in studies of guinea pig liver and human erythrocytes (Hers & Kusaka 1953; Beutler & Guinto 1973). The human enzyme has been cloned and studied (Cabezas et al. 2005; Rodrigues et al. 2014). DAK/TKFC also catalyzes the phosphorylation of dihydroxyacetone (DHA) to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), not a necessary step in fructose catabolism, but possibly functional on exogenous DHA. Triokinase activities on GA and DHA require homodimeric enzyme formed by two-domain subunits, where triose binds to one subunit and ATP to the other, each in a different domain.
DAK/TKFC is a bifunctional enzyme which, besides the ATP/Mg-dependent phosphorylation of GA and DHA, also catalyses, in presence of Mn2+, a unisubstrate reaction splitting flavin-adenine dinucleotide (FAD) into riboflavin cyclic 4',5'-phosphate (cyclic FMN) and AMP (Cabezas et al. 2005; Rodrigues et al. 2014).
In addition, DAK/TKFC protein binds to MDA5 and acts as a negative regulator of MDA5-mediated induction of IFN-alpha/beta pathways (Diao et al. 2007). Potentially related to this TKFC effect are the observations that hepatic DAK/TKFC levels correlate with outcome in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with interferon (Perdomo et al. 2012), and that a DAK/TKFC serum peptide is a predictor of disease severity in hepatitis B patients (Xu et al. 2013).
DAK/TKFC is a bifunctional enzyme which, besides the ATP/Mg-dependent phosphorylation of GA and DHA, also catalyses, in presence of Mn2+, a unisubstrate reaction splitting flavin-adenine dinucleotide (FAD) into riboflavin cyclic 4',5'-phosphate (cyclic FMN) and AMP (Cabezas et al. 2005; Rodrigues et al. 2014).
In addition, DAK/TKFC protein binds to MDA5 and acts as a negative regulator of MDA5-mediated induction of IFN-alpha/beta pathways (Diao et al. 2007). Potentially related to this TKFC effect are the observations that hepatic DAK/TKFC levels correlate with outcome in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with interferon (Perdomo et al. 2012), and that a DAK/TKFC serum peptide is a predictor of disease severity in hepatitis B patients (Xu et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
GA3P [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
GA [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70349
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
D-glyceraldehyde
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate(2-)
ADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70349