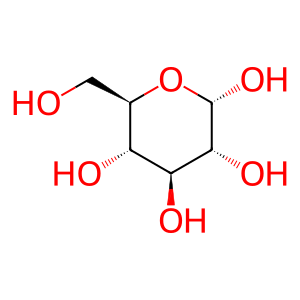
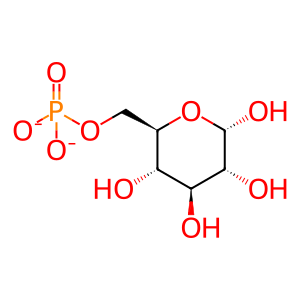
Reaction: HK1,2,3,GCK,HKDC1 phosphorylate Glc to form G6P
- in pathway: Glycolysis
Cytosolic glucokinase and the three isoforms of hexokinase catalyze the irreversible reaction of glucose and ATP to form glucose 6 phosphate and ADP. In the body glucokinase is found only in hepatocytes and pancreatic beta cells. Glucokinase and the hexokinase enzymes differ in that glucokinase has a higher Km than the hexokinases and is less readily inhibited by the reaction product. As a result, glucokinase should be inactive in the fasting state when glucose concentrations are low but in the fed state should have an activity proportional to glucose concentration. These features are thought to enable efficient glucose uptake and retention in the liver, and to function as a sensor of glucose concentration coupled to insulin release in pancreatic beta cells (Thorens 2001). Glucokinase mutations are associated with MODY2, a heritable early onset form of type II diabetes (Tanizawa et al. 1991; Takeda et al. 1993). Three human hexokinase enzymes, which differ in their expression patterns have been characterized, HK1 (Aleshin et al. 1998), HK2 (Lehto et al. 1995), and HK3 (Rijksen at al. 1982).
An additional gene product, HKDC1, although not classically associated with glycolysis in adult tissues, has hexokinase activity in vitro and may have a role in glucose homeostasis during embryonic development (Guo et al. 2015; Pusik et al. 2019; Zapater et al. 2022). HKDC1 has therefore been annotated here as a candidate member of the set of enzymes that mediates glucose phosphorylation.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
G6P [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Glc [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70420
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
alpha-D-glucose
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
ADP(3-)
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70420