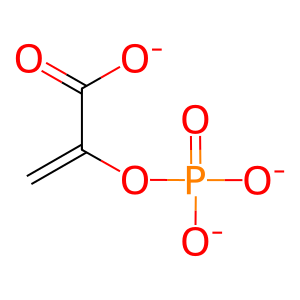
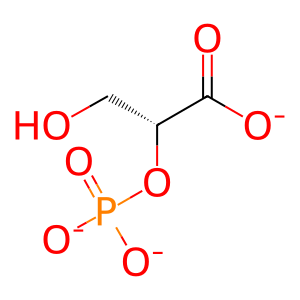
Reaction: Enolase dimers (ENO1,2,3) convert PEP to 2PG
- in pathway: Gluconeogenesis
Cytosolic enolase dimers catalyze the reversible reaction of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and water to form 2-phosphoglycerate (2PG). Three enolase isozymes have been purified and biochemically characterized. The alpha isoform (ENO1) is widely expressed (Giallongo et al. 1986). The beta isoform (ENO3) is expressed in muscle. Evidence for its function in vivo in humans comes from studies of a patient in whom a point mutation in the gene encoding the enzyme was associated specifically with reduced enolase activity in muscle extracts, and with other symptoms consistent with a defect in glycolysis (Comi et al. 2001). The gamma isoform of human enolase (ENO2) is normally expressed in neural tissue. It is not known to have distinctive biochemical functions, but is of possible clinical interest as a marker of some types of neuroendocrine and lung tumors (McAleese et al. 1988). A fourth candidate isozyme, ENO4, has been identified in the human and mouse genomes. The mouse form of the gene encodes a protein with enolase activity that is expressed in sperm and whose disruption is associated with abnormal sperm morphology (Nakamura et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
2PG [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
PEP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70494
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
phosphonatoenolpyruvate
Reaction output - small molecules:
2-phosphonato-D-glycerate(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70494