Reaction: PC catalyzes the carboxylation of PYR to form OA
- in pathway: Gluconeogenesis
Mitochondrial pyruvate carboxylase (PC) catalyzes the irreversible reaction of pyruvate (PYR), bicarbonate (HCO3-), and ATP to form oxaloacetate (OA), ADP, phosphate, (Pi) and H+. The enzyme is biotinylated and is active as a tetramer. Its structure and function have been characterized in detail (Jitrapakdee et al. 2008; Jitrapakdee & Wallace 1999), and both normal and defective forms of the human enzyme have been described (Carbone & Robinson 2003).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [mitochondrial matrix]
ADP [mitochondrial matrix]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
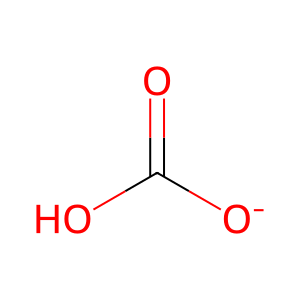
OA [mitochondrial matrix]
HCO3- [mitochondrial matrix]
ATP [mitochondrial matrix]
PYR [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70501
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydrogencarbonate
ATP(4-)
pyruvate
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
hydron
oxaloacetate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70501