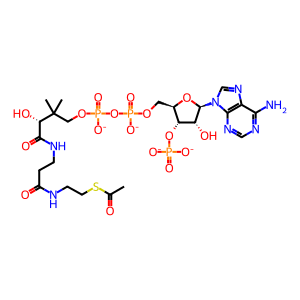
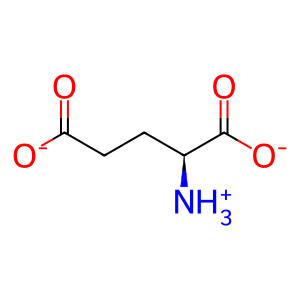
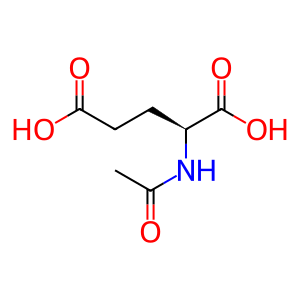
Reaction: glutamate + acetyl CoA => N-acetyl glutamate + CoA
- in pathway: Urea cycle
Mitochondrial N acetylglutamate synthetase (NAGS) catalyzes the reaction of glutamate and acetyl-CoA to form N-acetylglutamate and CoA. NAGS is activated by arginine and the N-acetylglutamate produced in the reaction in turn is required to activate carbamoyl synthetase I. Consistent with this regulatory role in urea synthesis, NAGS mutations in humans are associated with hyperammonemia (Caldovic et al. 2002; Morizono et al. 2004).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CoA-SH [mitochondrial matrix]
NAcGlu [mitochondrial matrix]
Ac-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Glu [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70542
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetyl-CoA(4-)
L-glutamate(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
N-acetyl-L-glutamic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70542