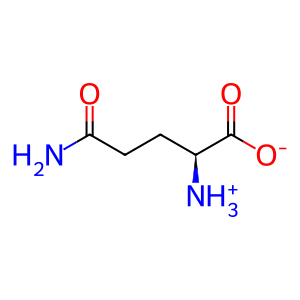
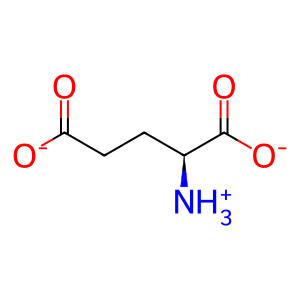
Reaction: glutamine + H2O => glutamate + NH4+ [GLS]
- in pathway: TP53 Regulates Metabolic Genes
Mitochondrial glutaminase (GLS) catalyzes the hydrolysis of glutamine to yield glutamate and ammonia. Two GLS enzymes have been identified, one abundantly expressed in the liver (GLS - Elgadi et al. 1999) and one abundantly expressed in kidney (GLS2 - Gomez-Fabre et al. 2000). Their biochemical properties are similar. The enzymes are inferred to function as dimers based on unpublished crystallographic data for GLS (PDB 3CZD) and studies of glutaminase enzyme purified from Ehrlich Ascites cells (Quesada et al. 1988).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
NH4+ [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Glu [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Gln [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
NH4+ [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Glu [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Gln [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
NH4+ [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Glu [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Gln [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70609
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-glutamine zwitterion
water
L-glutamine zwitterion
water
L-glutamine zwitterion
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
ammonium
L-glutamate(1-)
ammonium
L-glutamate(1-)
ammonium
L-glutamate(1-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70609