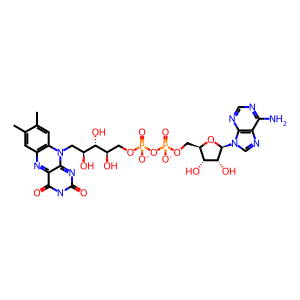
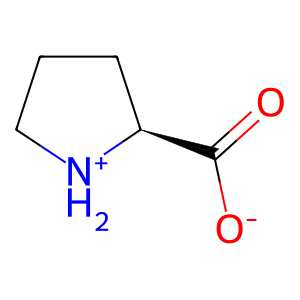
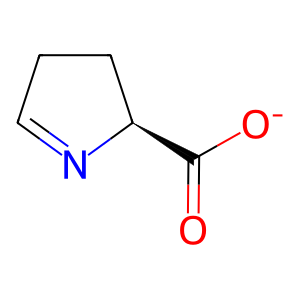
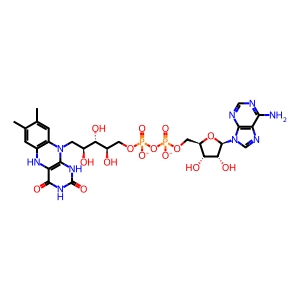
Reaction: PRODH oxidises L-Pro to 1PYR-5COOH
- in pathway: Proline catabolism
The dehydrogenation (oxidation) of proline to L-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate coupled to the conversion of FAD to FADH2 is the first step in proline breakdown (Bender et al. 2005). Proline dehydrogenase (PRODH), the enzyme that catalyzes this reaction, is found in liver, kidney, and brain cells, where it is tightly bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
1PYR-5COOH [mitochondrial matrix]
FADH2 [mitochondrial inner membrane]
FAD [mitochondrial inner membrane]
L-Pro [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70670
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
FAD(3-)
L-proline zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
(S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate
FADH2(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70670