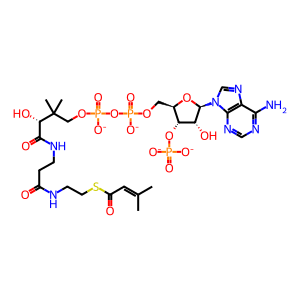
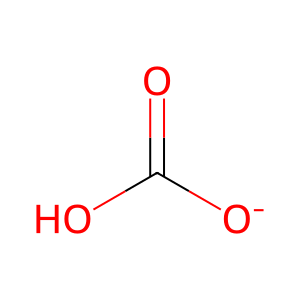
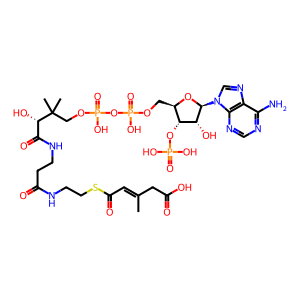
Reaction: beta-methylcrotonyl-CoA + ATP + CO2 <=> beta-methylglutaconyl-CoA + ADP + orthophosphate + H2O [MCCA]
- in pathway: Branched-chain amino acid catabolism
Methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase (MCCA) catalyzes the reversible reaction of beta-methylcrotonyl-CoA, ATP, and CO2 to form beta-methylglutaconyl-CoA, ADP, orthophosphate, and H2O. Active MCCA is composed of two polypeptides, MCCA1 and MCCA2 (Baumgartner et al. 2001; Holzinger et al. 2001). The enzyme has been purified from fibroblast mitochondria. By analogy to the more thoroughly studied bovine homologue, MCCA is thought to be a hexamer of six MCCA1:MCCA2 dimers, and the MCCA1 polypeptide is thought to have a biotin moiety covalently bound to lysine residue 681. Localization of the complex to the mitochondrial inner membrane is inferred from studies of the bovine homologue (Hector et al. 1980). Mitochondrial import of MCCA1 and 2 is associated with removal of aminoterminal mitochondrial targeting sequences (Stadler et al. 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [mitochondrial matrix]
ADP [mitochondrial matrix]
bMC-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
bMC-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
HCO3- [mitochondrial matrix]
ATP [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70773
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
3-methylbut-2-enoyl-CoA(4-)
hydrogencarbonate
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
trans-3-methylglutaconyl-CoA
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70773