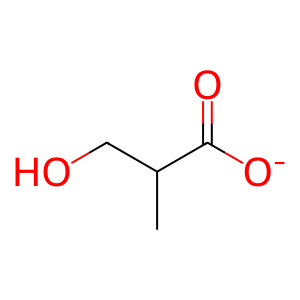
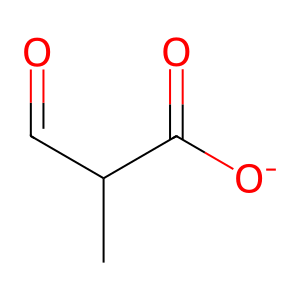
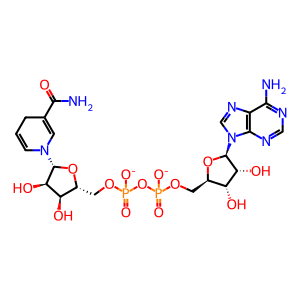
Reaction: beta-hydroxyisobutyrate + NAD+ <=> methylmalonyl semialdehyde + NADH + H+
- in pathway: Branched-chain amino acid catabolism
Mitochondrial 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase (HIBADH) catalyzes the reversible reaction of beta-hydroxyisobutyrate and NAD+ to form methylmalonyl semialdehyde and NADH + H+. The biochemical properties of human HIBADH are inferred from those of its better-studied porcine homologue (Robinson and Coon 1957). Unpublished crystallographic studies (PDB 2GF2) have shown the active enzyme to be a tetramer of HIBADH polypeptides whose aminoterminal 40 residues, a mitochondrial targeting sequence, have been removed.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
2M3OPROA [mitochondrial matrix]
NADH [mitochondrial matrix]
NAD+ [mitochondrial matrix]
bHIBA [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70885
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
NAD(1-)
3-hydroxyisobutyrate
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
2-methyl-3-oxopropanoate
NADH(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70885