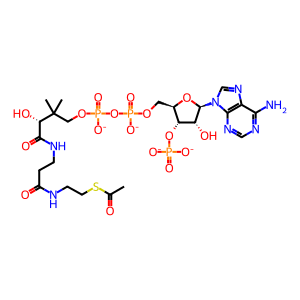
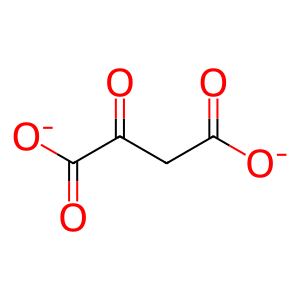
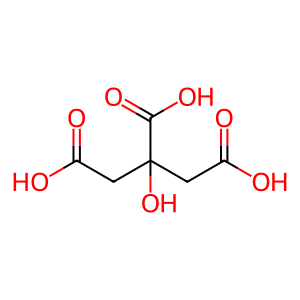
Reaction: Acetyl-CoA + H2O + Oxaloacetate => Citrate + CoA
- in pathway: Citric acid cycle (TCA cycle)
Mitochondrial citrate synthase dimer catalyzes the irreversible reaction of acetyl-CoA, water, and oxaloacetate to form citrate and coenzyme A. This reaction is the entry point of two-carbon units into the citric acid cycle. The reaction is subject to allosteric regulation. The gene encoding the human enzyme has been cloned (Goldenthal et al. 1998), but the enzyme has not been characterized in detail - its properties are inferred from those of the well-studied homologous pig enzyme (e.g., Morgunov and Srere 1998).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CoA-SH [mitochondrial matrix]
CIT [mitochondrial matrix]
Ac-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
OA [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70975
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetyl-CoA(4-)
oxaloacetate(2-)
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
citric acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70975