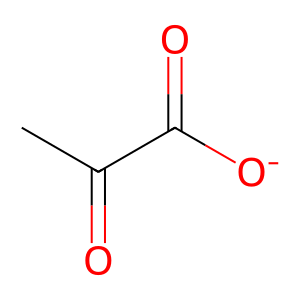
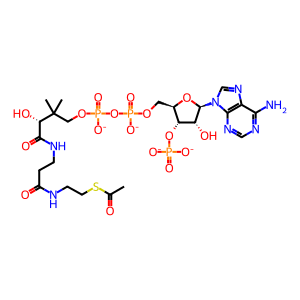
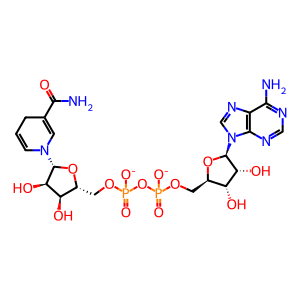
Reaction: lipo-PDH decarboxylates PYR to Ac-CoA
- in pathway: Pyruvate metabolism
The mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate, CoASH, and NAD+ to form acetylCoA, CO2, and NADH. The enzyme complex contains multiple copies of three different proteins, E1 alpha, E1 beta, E2, and E3, each with distinct catalytic activities (Reed and Hackert 1990; Zhou et al 2001). The reaction starts with the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate catalyzed by E1 alpha and beta (pyruvate dehydrogenase). Lipoamide cofactor associated with E1 is reduced at the same time. Next, the acetyl group derived from pyruvate is transferred to coenzyme A in two steps catalyzed by E2 (dihydrolipolyl transacetylase). Finally, the oxidized form of lipoamide is regenerated and electrons are transferred to NAD+ in two steps catalyzed by E3 (dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase). The biochemical details of this reaction have been worked out with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and subunits purified from bovine tissue and other non-human sources. Direct evidence for the roles of the corresponding human proteins comes from studies of patients expressing mutant forms of E1 alpha (Lissens et al. 2000), E1 beta (Brown et al. 2004), E2 (Head et al. 2005), and E3 (Brautigam et al. 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Ac-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
NADH [mitochondrial matrix]
CO2 [mitochondrial matrix]
CoA-SH [mitochondrial matrix]
NAD+ [mitochondrial matrix]
PYR [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-71397
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
NAD(1-)
pyruvate
Reaction output - small molecules:
acetyl-CoA(4-)
NADH(2-)
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-71397