Reaction: glycogen-glycogenin-1 + n orthophosphate => limit dextrin-glycogenin-1 + n D-glucose 1-phosphate [PYGM,PYGB]
- in pathway: Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis)
The PYGM and PYGB forms of glycogen phosphorylase catalyze the reaction of orthophosphate and glycogen-glycogenin 1 to form D-glucose 1-phosphate and limit dextrin-glycogenin 1. This reaction occurs on the surfaces of cytosolic glycogen granules. The phosphorylated forms of PYGM and PYGB dimers (a form) are catalytically active; the non-phosphorylated dimers (b form) become active when complexed with AMP. In the body, this reaction takes place in tissues other than the liver where its sensitivity to AMP allows glucose mobilization in response to acute energy needs of the individual cell, and hormonally mediated phosphorylation can stimulate increased glucose production, still for use by the individual producing cell, in response to stress signals. These reactions have not been characterized in detail but are inferred to occur from the very close similarity among PGYM, PGYB, and PGYL (Newgard et al. 1989; Rath et al. 2000).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
G1P [cytosol]
Pi [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-71515
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
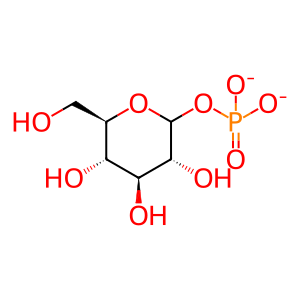
hydrogenphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
D-glucopyranose 1-phosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-71515