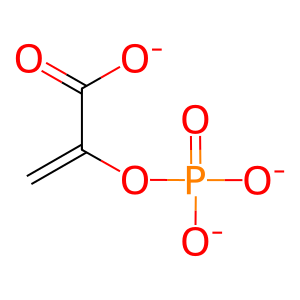
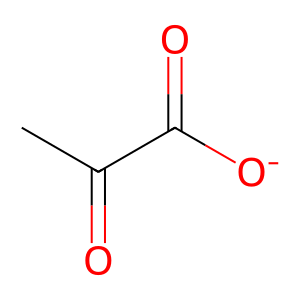
Reaction: phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP => pyruvate + ATP
- in pathway: Glycolysis
Cytosolic pyruvate kinase catalyzes the transfer of a high-energy phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, forming pyruvate and ATP. This reaction, an instance of substrate-level phosphorylation, is essentially irreversible under physiological conditions.
Four isozymes of human pyruvate kinase have been described, L, R, M1 and M2. Isozymes L and R are encoded by alternatively spliced transcripts of the PKLR gene; isozymes M1 and M2 are encoded by alternatively spliced transcripts of PKM2. In the body, L pyruvate kinase is found in liver (Tani et al. 1988), R in red blood cells (Kanno et al. 1991), M1 in muscle, heart and brain (Takenaka et al. 1991), and M2 in early fetal tissues and tumors (e.g., Lee et al. 2008). In all cases, the active form of the enzyme is a homotetramer, activated by fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (Valentini et al. 2002; Dombrauckas et al. 2005). Mutations in PKLR have been associated with hemolytic anemias (e.g., Zanella et al. 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
ATP [cytosol]
PYR [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
PEP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-71670
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
ADP(3-)
phosphonatoenolpyruvate
Reaction output - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
pyruvate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-71670