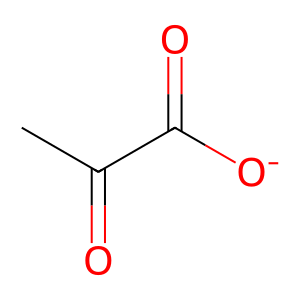
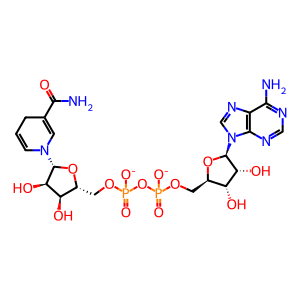
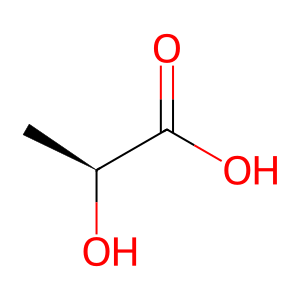
Reaction: LDH tetramer reduces PYR to LACT
- in pathway: Pyruvate metabolism
Cytosolic lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) catalyzes the freely reversible reaction of pyruvate (PYR) and NADH + H+ to form lactate (LACT) and NAD+. In liver parenchymal cells, this reaction allows lactate from red blood cells and exercising muscle to be converted to pyruvate which in turn is typically used for gluconeogenesis which also consumes the NADH from the reaction.
Lactate dehydrogenase is active as a tetramer. Two isoforms of lactate dehydrogenase, A and B, are widely expressed in human tissues, and all five tetramers - A4, A3B, A2B2, AB3, and B4 - are found (Read et al. 2001; Sakai et al. 1987; Yu et al. 2001). A third isoform, C, and its tetramer, C4, are found in testis (Millan et al. 1987; LeVan & Goldberg 1991). A fourth isoform, LDHAL6A, is less fully characterized than these others but limited data suggest that it may be testis-specific (Chen et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
LACT [cytosol]
NAD+ [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
PYR [cytosol]
NADH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-71849
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
pyruvate
NADH(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
(S)-lactic acid
NAD(1-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-71849