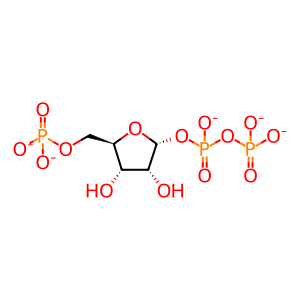
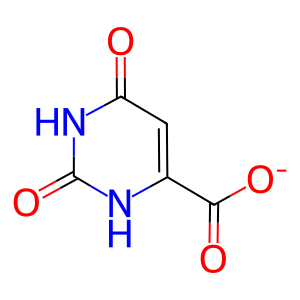
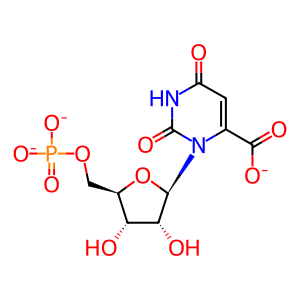
Reaction: UMPS dimer transfers phosphoribosyl group to ORO to form OMP
- in pathway: Pyrimidine biosynthesis
The synthesis of orotidine 5'-monophosphate (OMP) from orotate and 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate (PRPP) is catalyzed by the orotate phosphoribosyltransferase activity of the bifunctional "uridine monophosphate synthetase (orotate phosphoribosyl transferase and orotidine 5'-decarboxylase)" protein. The reaction itself is freely reversible, but is pulled in the forward direction in vivo by the irreversible hydrolysis of pyrophosphate. While purified human protein has not been characterized in detail, the close similarity of the human gene to that encoding the well-studied hamster protein, and the demonstration that mutations in the human gene are associated with failure to convert orotate to UMP in vivo, provide convincing evidence that the human uridine monophosphate synthetase protein indeed catalyzes these two reactions (McClard et al. 1980; Suchi et al. 1997). The active form of the human protein is a dimer (Yablonski et al. 1996; Wittmann et al. 2008).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
OMP [cytosol]
PRPP [cytosol]
ORO [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-73567
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
5-O-phosphonato-alpha-D-ribofuranosyl diphosphate(5-)
orotate
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
orotidine 5'-phosphate(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-73567