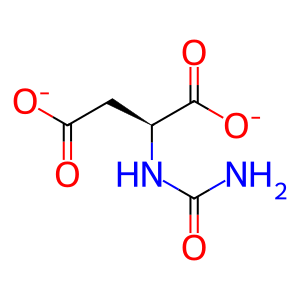
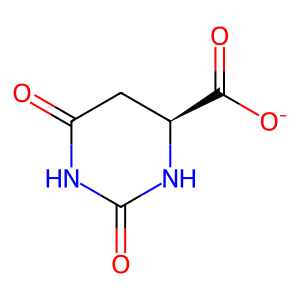
Reaction: CAD hexamer dehydrates N-carb-L-Asp to (S)-DHO
- in pathway: Pyrimidine biosynthesis
The synthesis of dihydroorotate from N-carbamoyl L-aspartate is catalyzed by the dihydroorotase activity of cytosolic trifunctional CAD (carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 2, aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydroorotase) protein. This activity has not been directly demonstrated in experimental studies of the purified human protein, but has been inferred from the behavior of the purified hamster protein and the high degree of sequence similarity between the cloned hamster and human genes (Iwahana et al. 1996). Also on the basis of this similarity, the active human protein is annotated as a hexamer (Lee et al. 1985).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
(S)-DHO [cytosol]
N-carb-L-Asp [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-73571
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate(2-)
hydron
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
(S)-dihydroorotate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-73571