Reaction: CAD hexamer transforms CAP to N-carb-L-Asp
- in pathway: Pyrimidine biosynthesis
The synthesis of N-carbamoyl L-aspartate from carbamoyl phosphate and L-aspartate is catalyzed by the aspartate carbamoyltansferase activity of cytosolic trifunctional CAD (carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 2, aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydroorotase) protein (Ito and Uchino 1973; Iwahana et al. 1996). The purified human protein is active in several different oligomerization states as is its Syrian hamster homologue. The most abundant form of the latter is a hexamer, and the active human protein is annotated as a hexamer by inference (Ito and Uchino 1973; Lee et al. 1985).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
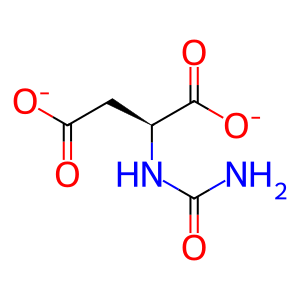
N-carb-L-Asp [cytosol]
Pi [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
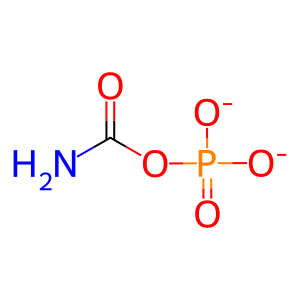
CAP [cytosol]
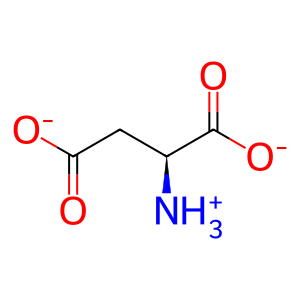
L-Asp [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-73573
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
carbamoyl phosphate(2-)
L-aspartate(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate(2-)
hydrogenphosphate
hydron
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-73573