Reaction: SCD5 desaturates ST-CoA to OLE-CoA
- in pathway: Fatty acyl-CoA biosynthesis
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 5 (SCD5, also known as acyl-CoA desaturase 4), located on the ER membrane, utilises O2 and electrons from reduced ferrocytochrome b5 (Fe(2+)Cb5) to catalyse the insertion of a double bond into a range of fatty acyl-CoA substrates. SCD5 is most abundant in brain and pancreas. The reaction annotated here shows stearoyl-CoA (ST-CoA) desaturation to oleoyl-CoA (OLE-CoA). Studies of tagged recombinant enzyme overexpressed in transiently transfected cells suggest that the enzyme forms dimers and higher oligomers (Wang et al. 2005; Zhang et al. 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Fe(3+)Cb5 [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
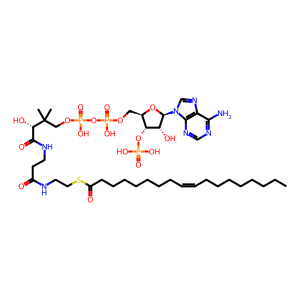
OLE-CoA [cytosol]
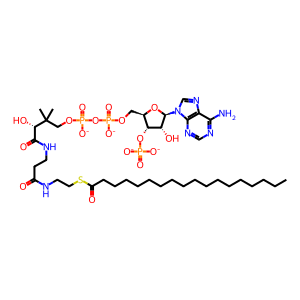
ST-CoA [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
Fe(2+)Cb5 [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8847579
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
stearoyl-CoA(4-)
hydron
ferrocytochrome b5
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
ferricytochrome b5
water
oleoyl-CoA
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8847579