Reaction: AWAT2 transfers PALM from PALM-CoA to HXOL, forming palmityl palmitate ester
- in pathway: Wax biosynthesis
AWAT2 (Acyl-CoA wax alcohol acyltransferase 2, also known as MFAT and DC4) associated with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane catalyzes the reaction of HXOL (hexadecanol) and PALM-CoA (palmitoyl-CoA) to form the wax monoester palmityl palmitate. The enzyme also acts efficiently on other long-chain fatty alcohols and fatty acyl CoAs. It is abundant in skin and is thought to play a central role in the synthesis of wax molecules that protect the skin from drying (Cheng & Russell 2004; Turkish et al. 2005; Yen et al. 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
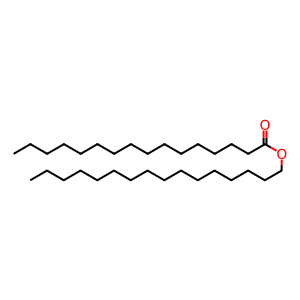
PALM-PALM [cytosol]
CoA-SH [cytosol]
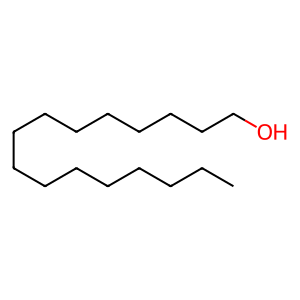
HXOL [cytosol]
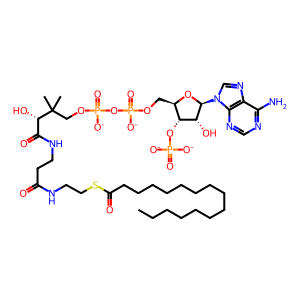
PALM-CoA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8848582
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hexadecan-1-ol
palmitoyl-CoA(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
palmityl palmitate
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8848582