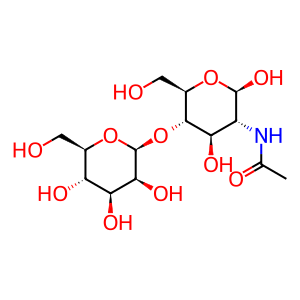
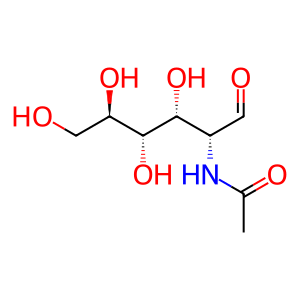
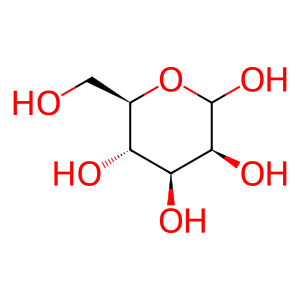
Reaction: MANBA hydrolyses GlcNAc:Man
- in pathway: Lysosomal oligosaccharide catabolism
Beta-mannosidase (MANBA) is the final exoglycosidase in the degradation pathway for N-linked oligosaccharides of glycoproteins, cleaving the beta-mannoside linkage of the disaccharide Man-1,4-GlcNAc (Alkhayat et al. 1998, Percheron et al. 1992). Defects in MANBA causes beta-mannosidosis (MIM:248510), a lysosomal storage disease of glycoprotein catabolism. A wide range of symptoms are observed, dependent on age of onset. The disease is associated with various degrees of mental retardation in most of the cases, hearing loss and speech impairment, hypotonia, epilepsy and peripheral neuropathy (Alkhayat et al. 1998, Molho-Pessach et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
GlcNAc [lysosomal lumen]
Man [lysosomal lumen]
GlcNAc:Man [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8853710
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
beta-D-Manp-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpNAc
Reaction output - small molecules:
aldehydo-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
D-mannopyranose
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8853710